Chapter 12: harmonisation of rules on food treatment with ionizing radiation
Treatment of food and food ingredients with ionizing radiation is a method that is increasingly used worldwide as a way of preserving food. The PLAC III project has provided support to the competent institutions of Serbia in harmonizing the national legislation with the EU rules in that area that falls under the scope of the Negotiation Chapter 12.
Support was provided to the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Agriculture, Water Management and Forestry, in order to harmonise national laws with relevant Union acquis and prepare the national administration for the implementation of harmonised legislation. In Serbia, the Law on Food Safety shares competence between the Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Health, the use of radiation sources is defined by the Law on Radiation and Nuclear Security and Safety, while market entry is regulated by the Rulebook on conditions under which food and general use items preserved by ionizing radiation may be placed on the market.
In the EU, the treatment of food with ionizing radiation is regulated by the Framework Directive 1999/2/EC, which prescribes general and technical aspects, labelling of irradiated food and the conditions for authorising food irradiation. Based on that directive, a list of national authorisations for food or food ingredients that can be treated with ionizing radiation was made, as well as a list of facilities in Member States that have an authorization for food irradiation. Implementing Directive 1999/3/EC stipulates that in the EU dried aromatic herbs, spices and vegetable seasonings can be treated with ionizing radiation, and sets 10 kGy as the maximum radiation dose.
Project experts Lenče Jovanovska and Jelena Vračar Filipović presented the results of the legal gap analysis of Serbian legislation, recommendations for harmonisation and proposals of bylaws at a workshop held on 26 January 2022.
Harmonisation has been proposed through the development of a legal basis (amendments to the Law on Food Safety), drafting of two rulebooks as well as procedures for official controls of irradiated food, and the establishment of accredited laboratory methods. According to Jovanovska, the existing Rulebook is a good basis for harmonisation with the relevant EU legislation.
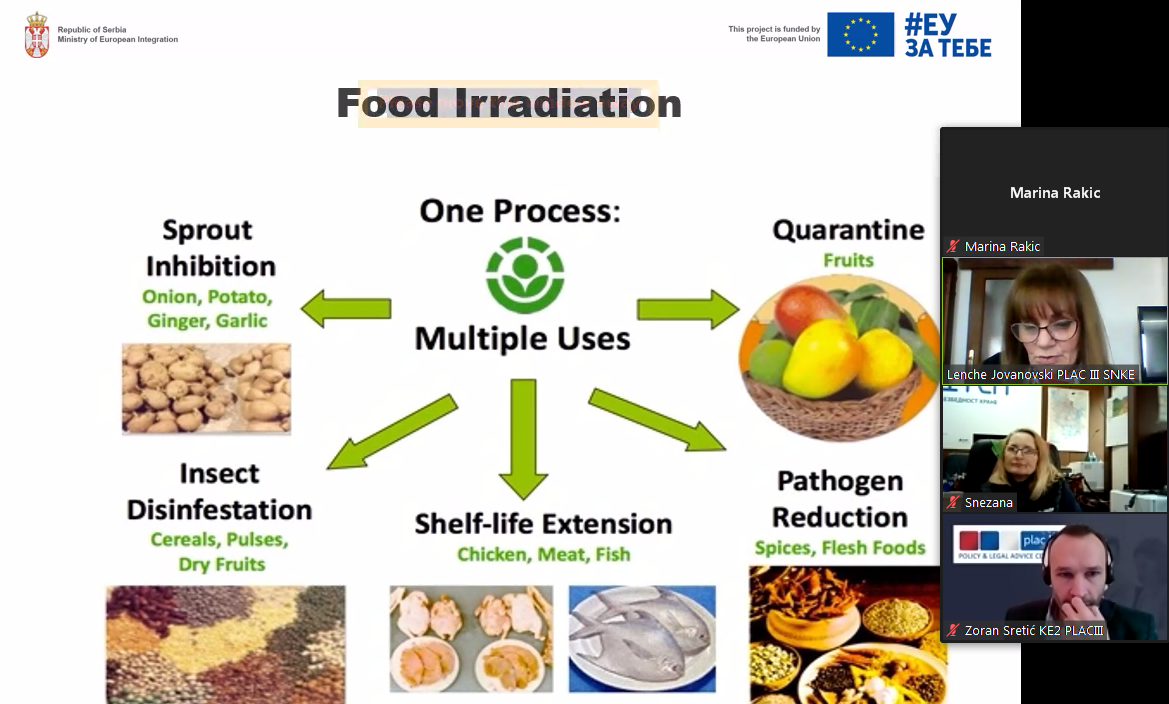
Jovanovska stated that there is a growing trend in the world of use of ionizing irradiation as a food treatment, which is a type of food conservation, mostly in the United States and the Asia-Pacific region. Of the 700,000 tons of agricultural and food products treated this way annually in the world, only one percent is in Europe. According to the European Commission’s report, in the period 2018-2019 a total of 7,892 tons of food was treated with radiation, of which 80 percent in Belgium. Food radiation as a form of conservation was supported by the World Health Organization, the American Dietetic Association and the EU Scientific Committee.
Expert Jelena Vračar Filipović presented a draft rulebook on the treatment of food with ionizing radiation, which refers to food suitable for human consumption. The Rulebook also prescribes the requirements for food labelling, as well as the requirements that the facility must meet in order to irradiate food in it. The recommendation made by the project experts was that the competent commission that will deal with that area should be multidisciplinary and include SRBATOM (Directorate for Radiation and Nuclear Safety of Serbia). Vračar Flipović also presented the procedures for official controls of food treated with ionizing radiation.
The workshop was attended by representatives of the Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Agriculture, Water Management and Forestry and the Vinča Institute of Nuclear Sciences.
Photo credit: EC - Audiovisual service